What is Conjunctivitis?
The conjunctiva is the thin clear tissue that lines over the white part of the eye and the inside of the eyelid. Commonly known as pink eye, conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva.
Types of Conjunctivitis
- Bacterial
- Viral
- Allergic
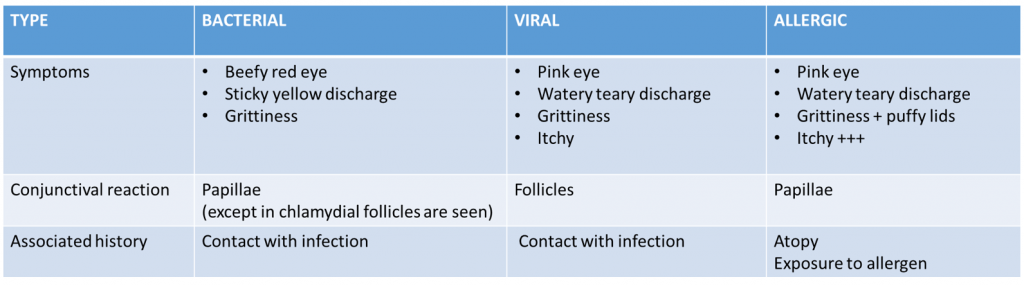
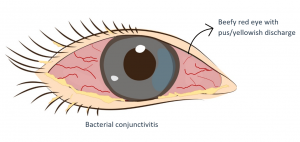
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Causes
Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae can cause this condition. These organisms may be spread from hand to eye contact, fomites, or oculo-genital contact with someone infected.
Neonatal conjunctivitis is usually caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia. It occurs in newborn’s whose eyes get infected after vaginal delivery by mothers affected with the condition.
Symptoms
- Beefy red eye
- Muco-purulent discharge (pus/whitish/yellowish/greenish) which may cause the eyelids to stick together.
- Grittiness, irritation and discomfort
- Tearing
Viral Conjunctivitis
Causes
Viruses such as Adenovirus and Herpes virus can cause this if the virus spreads to the eye. It can occur with symptoms of a cold, flu, or other respiratory infection. Viral conjunctivitis is known to be the most the contagious.
Symptoms
- Pinkish red eye
- Watery discharge
- Itchy, grittiness
- Irritation and discomfort
- Tearing
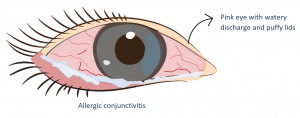
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Causes
Exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, animal dander, grass can cause this condition. It is frequently seen in patients with history of current or previous non-ocular allergic or atopic conditions (eczema, asthma, rhinitis).
Symptoms
- Lid swelling
- Pinkish red eye
- Watery, tearing discharge
- Intense itchy, grittiness
- Irritation and discomfort
- Blinking hard can be observed in kids
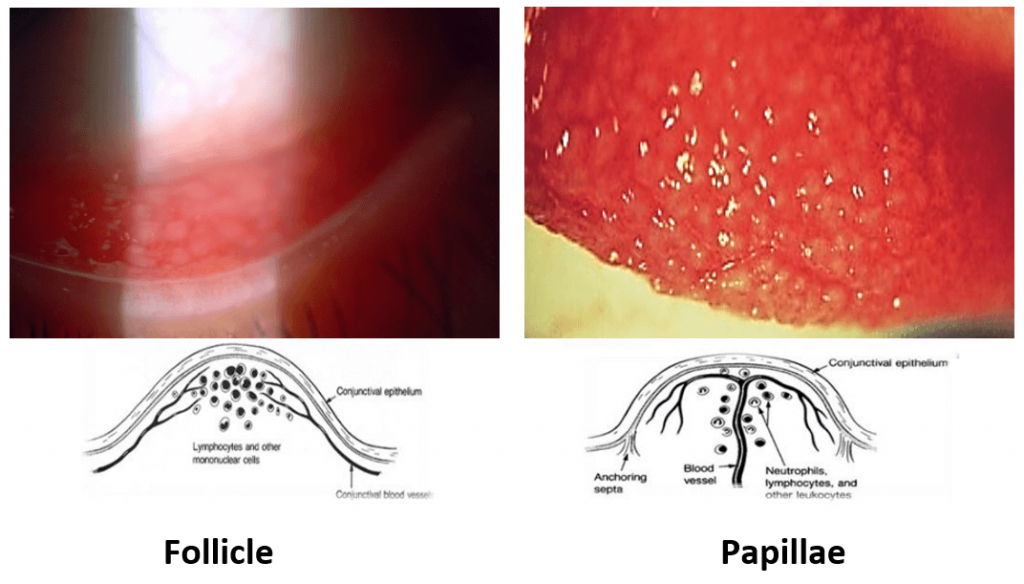
Summary of Types of Conjunctivitis
Reaction of conjunctiva lining the inner eyelid
What treatment options are available?
Bacterial and Viral Conjunctivitis
These can be treated with:
- Antibiotics/Anti-inflammatory medications
- Cold compresses – Reduces inflammation, helps with itching
- Artificial tears
Preventing spread
- Frequent hand washing
- Avoid sharing personal care objects such towels, cosmetics, etc
- Avoid contact with eyes
- Avoid shaking hands
Most cases are self-limiting within 1 to 2 weeks of presentation.
Allergic Conjunctivitis
It can be treated with:
- Allergen avoidance
- Cold compresses – Reduces inflammation, helps with itching
- Use of topical normal saline or lubricants (artificial tears) will reduce symptoms and may help dilute or flush away allergen and inflammatory mediators
- Immunotherapy – Anti histamines/Mast cell stabilizers