Nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) is the most common cause of persistent tearing in an infant/ young child, and can lead to infection and ocular discharge. Other causes range from mild, self-limiting conditions (eg. Viral or allergic conjunctivitis) to severe sight-threatening ocular emergencies (eg. ophthalmia neonatorum or eye infection in a newborn).
Causes of tearing in an infant/ young child
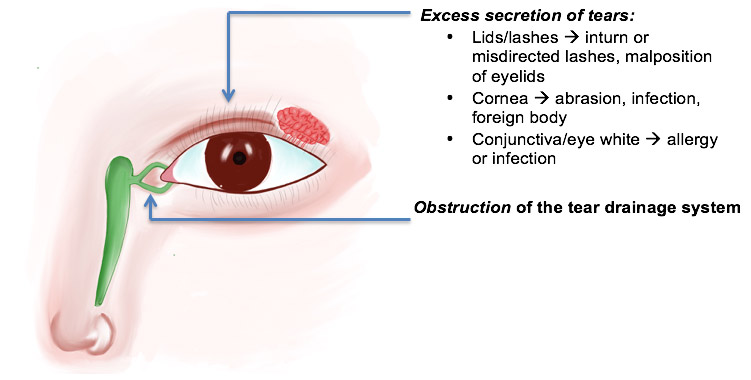
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO)
- A blocked tear duct stops the flow of tears from the eye down the lacrimal duct into the nose.
- Treatment:
- Massaging the eye
- Gently rubbing (massaging) the lacrimal sac will often help open the tear duct. You will usually need to do this four to six times a day. Your doctor will explain how to massage the lacrimal sac.
- Antibiotics
- If your child has an infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotic drops or ointment .
- Your child will only have surgery if other medical treatments do not work.
- Massaging the eye
Conjunctivitis/Pink Eye
- Pink eye is most often caused by viral infections associated with the common cold. It can also be caused by bacterial infections or allergies.
- Children with bacterial pink eye should take antibiotic drops or ointment. These are not needed for viral pink eye.
- Viral and bacterial pink eye are contagious. Prevent them from spreading with good hand washing and use of alcohol-based hand rubs.
- Pink eye should not cause any long term damage to a child’s vision.
- Seek medical attention if there is a change in vision, persistent redness, eye pain, or eyelid swelling.
Ophthalmia Neonatorum
This is an eye infection in a newborn child. There may be discharge and difficulty opening the eyes.
Causes
- Infections:
- Bacterial
Most common → Neisseria gonorrhea, Chlamydia - Viral
Herpes Simplex Virus (1-2 weeks after birth, vesicles on face, herpetic dendritic keratitis)
- Bacterial
- Samples of the discharge and swab of the conjunctival/eye white would be sent for microbiological diagnosis
- Blood work may need to be done if child has fever
Management
- Start broad spectrum antibiotic eyedrops
- Keep the eye clean with saline lavage
- Close follow up until cause known
- Tailor treatment according to infection results/sensitivity
- Child may also require oral antibiotics or even admission for medications if the cause is a bacteria that can cause damage to other organs.
To schedule an appointment or to know more about excessive tearing from your child’s eyes, please call 6777 6058. Alternatively please send us an enquiry.
